Emissions
“Grateful to serve for a better world.”
Magokichi Yamaoka, founder of Yanmar Co. Ltd., 1912
Yanmar strives in its work to develop and implement technologies and strategies to provide engines and equipment that meet the most stringent standards in effect: exhaust, noise and vibration emissions. Yanmar works closely with all its customers world-wide by providing any useful information pertaining to Emissions Compliance to continue the development and awareness of Yanmar Brand products. Yanmar does all this while providing the exceptional quality we have become known for.
Yanmar offers a lineup of nonroad engines that are compliant with the emission regulations established by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), European Union (EU) and the California Air Resources Board (CARB).
Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR)
Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) is an emission control strategy that offers significant reduction in NOX emissions from internal combustion engines. EGR was applied in light-duty gasoline and diesel-fueled vehicles in the mid-1970s and has transferred over to heavy-duty diesel engines from the early 2000s.
As of the 2008 model year, Yanmar has implemented EGR technology as part of its strategy for engines above 56 kW (75 hp) to meet the Tier 3 and Stage IIIA emissions regulations.
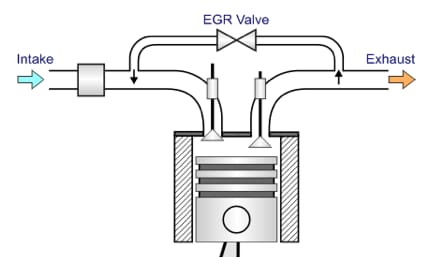
EGR is a method by which a portion of the engine’s exhaust gas is reintroduced to the combustion chamber through the intake system. The primary of effect of EGR, reduction of NOX, is created by reduction in combustion temperatures. Reduction of NOX does come with an increase to other exhaust constituents: PM, HC and CO emissions. However, Yanmar has taken the effort to implement additional engine modifications: electronically-controlled fuel injection, combustion and fuel injection optimization. Yanmar’s efforts also minimize the impact EGR would normally have on fuel economy and power density in order to provide you the same platform for all applications and ensuring compliance to the most stringent emissions regulations in effect.
The figure above is a representative schematic of a standard EGR System. Some engines employ the engine’s coolant to reduce the exhaust gas temperature prior to reintroduction to the combustion system further reducing NOX emissions.
Emissions Regulations
The EPA and EU are at the forefront for establishing the most stringent standards in effect today. Exhaust performance and testing requirements put the responsibility on the manufacturer to design and establish the most advanced engine control technology available. Implementation of the emissions regulations are in tiers with exhaust requirements becoming more stringent at each step.
Tier 1/Stage I and Tier 2/Stage II
Required manufacturers to optimize fuel injection and combustion performance; internal engine
modifications.
Tier 3/Stage IIIA
Required an approximate 60 percent reduction in particulate matter (PM) and a 50 percent reduction in
oxides of nitrogen (NOX) from first standards established in 1996.
Tier 4/Stage V
Requires manufacturers to further reduce both PM and NOX emissions by approximately 90 percent; nonroad
engines will be at near-zero levels.
Certificates
To help identify the appropriate certificate of conformity, you will need to:
- Locate the emissions control information label on the engine (valve cover).
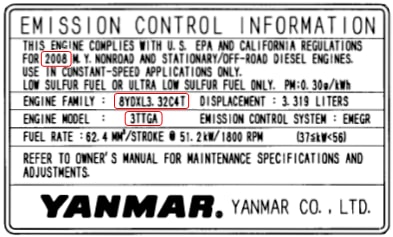
- Note your engine’s information.
- Model Year
- Engine Family
- Engine Model
- For CARB Executive Orders:
- Go to website http://www.arb.ca.gov/msprog/offroad/cert/cert.php
- Select Equipment Category: Offroad Compression-Ignition Engines (Diesel)
- Select Model Year: example “2008”
- Select: “Regular”
- Click Browse
- Select Manufacturer. Scroll to bottom of list and select all of the “Yanmar” company names.
- Click Submit
Example: Look for Engine Family 8YDXL3.32C4T and select Executive Order U-R-028-0403
Make sure to locate the engine model number on the executive order.
For EPA Engine Certification Data:
- Go to https://www.epa.gov/compliance-and-fuel-economy-data/annual-certification-data-vehicles-engines-and-equipment
- Download the Excel file corresponding to the requested engine type (nonroad compression ignition, marine compression ignition, etc.)
- Search for “Certificate #” by filtering “Yanmar” and “Engine Family”.

 Agriculture Equipment
Agriculture Equipment Compact Equipment
Compact Equipment Utility Task Vehicles
Utility Task Vehicles Industrial Engines
Industrial Engines Recreational Marine
Recreational Marine Marine Commercial
Marine Commercial Propulsion Engines (High Speed)
Propulsion Engines (High Speed) Propulsion Engines (Medium Speed)
Propulsion Engines (Medium Speed) Auxiliary Engines
Auxiliary Engines SCR System
SCR System Dual Fuel Engine
Dual Fuel Engine Two-stage Turbocharging System
Two-stage Turbocharging System Electric Propulsion System
Electric Propulsion System Net Cleaning Robot
Net Cleaning Robot Energy Systems
Energy Systems Compact Power Products
Compact Power Products YANMAR RePower
YANMAR RePower Genuine Parts
Genuine Parts